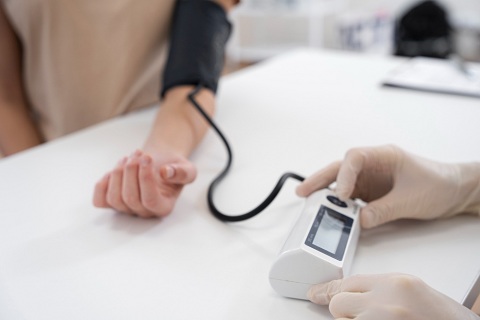
Low blood pressure, also known as hypotension, is a condition characterized by blood pressure levels that are lower than normal. While high blood pressure often receives more attention due to its association with various health risks, low blood pressure can also have significant impacts on a person’s well-being.
Low blood pressure, also known as hypotension, occurs when the systolic pressure is below 90 mm Hg, and the diastolic pressure is below 60 mm Hg. While some individuals naturally have low blood pressure without experiencing any adverse effects, others may face symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating.
Effective Management Strategies
Hydration Is Key
Ensuring adequate hydration is crucial in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. Encourage regular intake of water and fluids, especially in hot weather or during physical activity.
Balanced Diet
A nutrient-rich diet plays a pivotal role in managing low blood pressure. Emphasize foods high in potassium, magnesium, and calcium, such as bananas, leafy greens, nuts, and dairy products.
Regular Exercise
Physical activity promotes cardiovascular health and helps regulate blood pressure. Encourage a mix of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises for optimal benefits.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can contribute to fluctuations in blood pressure. Encourage stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, and mindfulness practices.
Monitor Blood Pressure Regularly
Encourage individuals with low blood pressure to monitor their blood pressure regularly using a reliable blood pressure monitor. This helps track changes and enables timely interventions if needed.
How can I raise my low blood pressure at home?
Increase Salt Intake

Adding a bit more salt to your meals can help raise blood pressure. However, consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your salt intake, especially if you have other health conditions.
However, eating too much salt on a daily basis is very harmful for the kidney. If you suddenly have a sudden drop in blood pressure, you can take extra salt, but you must consult a doctor about eating excessive salt.
Avoid Alcohol

Limiting or avoiding alcohol can help prevent a further decrease in blood pressure.
Avoid Standing Up Quickly
When transitioning from sitting or lying down to standing, do so slowly to prevent a sudden drop in blood pressure.
Wear Compression Stockings
Compression stockings can help improve blood flow and prevent blood from pooling in your legs, thus raising blood pressure.
Engage in Physical Activity

Regular exercise, especially activities that involve standing up and moving, can help regulate blood pressure.
Eat Small, Frequent Meals
Consuming smaller meals more frequently can prevent blood pressure from dropping too low after eating.
Follow Medical Advice
Always follow the advice and treatment plan prescribed by your healthcare provider. Attend regular check-ups and communicate any concerns or changes in your health.
FAQs about low blood pressure
To raise your blood pressure quickly, you can try the following:
Drink more water to increase blood volume.
Eat salty foods or snacks.
Stand up slowly if you’ve been sitting or lying down.
Wear compression stockings to improve blood flow.
Fruits that are rich in potassium, such as bananas, oranges, and avocados, are beneficial for low blood pressure as they help regulate blood pressure levels.
When blood pressure is low, it can cause symptoms like dizziness, fainting, fatigue, blurred vision, and a rapid or irregular heartbeat. In severe cases, low blood pressure can lead to shock or organ damage.
A blood pressure reading of 110/60 is considered within the normal range for most adults. However, it’s essential to consider individual factors and symptoms when assessing blood pressure levels.
Lowering blood pressure quickly in just 5 minutes may not be possible, but you can try relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or gentle exercise like walking to help lower stress levels and promote better blood pressure regulation over time. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice on managing blood pressure.
Conclusion
Managing low blood pressure requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medication management, and awareness of potential complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for low blood pressure, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their overall health and well-being.