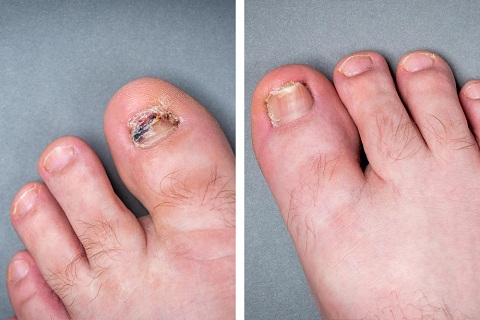
Nail fungus, medically known as Tinea Unguium, is a commonly affects the great toe nails but other nalils are also affected . It is characterized by the gradual discoloration, thickening, and distortion of the nails. Here there is invasion of the nail plates by the dermatophytes. Tinea Unguium is largely a disease of the adults, but children, especially those in institutions and in households where the adults are infected with T. rubrum, may be infected from time to time. In this article, we delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, prevention methods, and more surrounding this condition.
Causes of Tinea Unguium
Tinea Unguium is primarily caused by dermatophytes, a group of fungi that thrive in warm and moist environments. The most commonly involved species is trichophyton rubrum. T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes var. interdigitale and E. floccosum are the common dermatophytes known to cause this condition with associated foot and hand infections. The fungus gets entry through the free edge of the nail and progresses to the root. These fungi can enter the skin through tiny cuts or separations between the nail and the nail bed. Factors such as poor foot hygiene, wearing tight shoes, sharing personal items like nail clippers, and walking barefoot in public areas increase the risk of developing nail fungus.
Manytimes toenails are usually affected, but in AIDS patients superficial white onychomycosis of both toe and fingernails has been reported.
Symptoms of Tinea Unguium
The symptoms of nail fungus may vary, but commonly include:
- Nail discoloration: Nails may turn yellow, brown, or white.
- Thickened nails: Nails may become thicker than usual.
- Brittle or crumbling nails: Nails may become brittle and prone to crumbling and rough friable.
Diagnosis of Tinea Unguium
Diagnosing nail fungus usually involves a physical examination of the affected nails and may include laboratory tests such as a fungas may be demonstrated in nail section and nail dust by microscopic examintaion or by culture.
Prevention of Tinea Unguium

Preventive measures include practicing good foot hygiene, avoiding sharing personal items, wearing breathable footwear, keeping nails clean and trimmed, and avoiding walking barefoot in public places.
Complications
If left untreated, nail fungus can spread to other nails or skin and may lead to secondary bacterial infections. A traumatized nails and nails of elderly people are more susceptible to infection
Home Remedies
While some home remedies like vinegar soak, tea tree oil, or baking soda paste are often suggested for nail fungus, their effectiveness varies, and they are not a substitute for medical treatment.
Vinegar Soak:
Vinegar, particularly apple cider vinegar, is believed to have antifungal properties. Dilute vinegar with water in equal parts and soak the affected nails for 15-20 minutes daily. This acidic environment may help inhibit the growth of fungi.
Tea Tree Oil:
Tea tree oil is renowned for its antimicrobial properties, including antifungal effects. Apply a drop or two of tea tree oil directly to the affected nails using a cotton swab or dropper. Repeat this process twice daily.
Baking Soda Paste:
Baking soda is known for its alkaline properties, which can create an inhospitable environment for fungi. Make a paste by mixing baking soda with a small amount of water. Apply the paste to the affected nails, leave it on for 10-15 minutes, then rinse off with warm water. Repeat this process daily.
Garlic:
Garlic contains allicin, a compound known for its antifungal and antibacterial properties. Crush a few cloves of garlic to extract the juice, then apply it directly to the affected nails. Leave it on for 30 minutes before rinsing off with warm water. Repeat this process daily.
Coconut Oil:
Coconut oil has antifungal properties and can help moisturize the nails and surrounding skin. Apply a small amount of coconut oil to the affected nails and massage gently. Leave it on overnight and rinse off in the morning. Repeat this process daily.
Oregano Oil:
Oregano oil contains thymol, a compound with potent antifungal properties. Mix a few drops of oregano oil with a carrier oil such as olive oil or coconut oil, then apply it to the affected nails. Leave it on for 30 minutes before rinsing off. Repeat this process twice daily.
Hydrogen Peroxide Soak:
Hydrogen peroxide is known for its antiseptic properties and may help eliminate fungi. Dilute hydrogen peroxide with water in equal parts and soak the affected nails for 10-15 minutes daily. Be cautious not to use concentrations higher than 3%, as it may cause irritation.
Lemon Juice:
Lemon juice contains citric acid, which has antifungal properties. Apply freshly squeezed lemon juice directly to the affected nails using a cotton ball or swab. Leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off with warm water. Repeat this process daily.
When to See a Doctor
It is advisable to consult a doctor if nail fungus persists despite home remedies, or if complications such as pain, swelling, or drainage occur.
Living with Tinea Unguium
Living with nail fungus can be challenging, but managing it effectively through proper hygiene and medical treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. It’s also essential to address any emotional impact it may have.
FAQs answers to Tinea Unguium
Yes, nail fungus can spread from person to person or from one nail to another.
The duration of tinea unguium can vary depending on the severity of the infection, the chosen treatment method, and individual factors. In general, treatment may take several weeks to several months to completely eradicate the fungus.
There is no significant difference between tinea unguium and onychomycosis; they are different terms used to refer to the same condition, which is a fungal infection of the nails.
The most common type of tinea unguium is caused by dermatophytes, a group of fungi that commonly infect the nails.
There is no single “fastest” way to kill nail fungus, as the effectiveness of treatment depends on various factors such as the severity of the infection and individual response to treatment. However, oral antifungal medications prescribed by a doctor are often considered one of the most effective ways to treat nail fungus, as they can target the infection systemically.
Conclusion
Tinea Unguium, or nail fungus, is a common condition that can affect anyone. While it may seem harmless initially, ignoring it can lead to complications. Seeking timely medical advice, practicing good foot hygiene, and following preventive measures are crucial steps in managing this condition effectively.