Tinea Barbae is a fungal infection that affects the bearded and moustache area of the face and neck in adults males. At our platform, we understand the importance of providing accurate and detailed information to help you better understand and manage this condition effectively.
What is Tinea Barbae?
Tinea Barbae, also known as barber’s itch or barber’s rash, is a fungal infection caused by various dermatophyte fungi. It primarily affects the bearded and moustache area of men’s faces and necks, particularly those who have close contact with contaminated hair clippers or other grooming tools.
Causes of Tinea Barbae
The primary cause of Tinea Barbae is the invasion of the hair follicles by dermatophyte fungi. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments and can easily spread through direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated objects such as towels, razors, or hair clippers.
Symptoms of Tinea Barbae
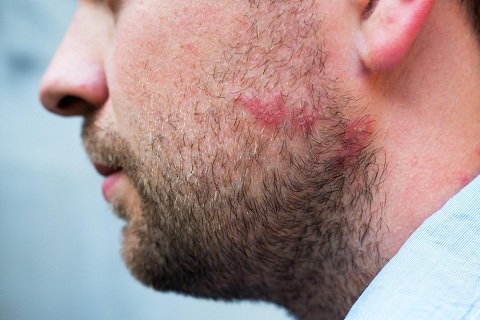
Itchy and Red Skin
One of the most common symptoms of Tinea Barbae is itching and redness in the affected area. This may start as a mild irritation but can progress to severe discomfort if left untreated. Redness and swelling of the affected skin
Pustules and Crusts
As the infection progresses, small pustules or pus-filled bumps may develop on the skin’s surface. These may eventually crust over and cause further irritation.
Hair Loss
In severe cases of Tinea Barbae, the infection can lead to hair loss in the affected area. This occurs as the fungi invade and damage the hair follicles, leading to weakened hair shafts and eventual loss.
Natural Treatment Options

Tea Tree Oil:
Tea tree oil is a natural antifungal agent that can help combat the fungus responsible for tinea barbae. Dilute tea tree oil with a carrier oil such as coconut oil and apply it directly to the affected area using a cotton swab or clean cloth. Repeat this process twice daily until the infection clears up.
Apple Cider Vinegar:
Apple cider vinegar has antifungal properties that can help eliminate the fungus causing tinea barbae. Mix equal parts apple cider vinegar and water, and apply the solution to the affected area using a cotton ball or pad. Leave it on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing it off with lukewarm water. Repeat this process once or twice daily until the infection resolves.
Garlic:
Garlic contains allicin, a compound with antifungal properties that can help treat tinea barbae. Crush a few garlic cloves to release the allicin, then apply the crushed garlic directly to the affected area. Leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing it off with water. Repeat this process daily until the infection improves.
Coconut Oil:
Coconut oil has natural antifungal properties and can help soothe irritated skin associated with tinea barbae. Apply coconut oil directly to the affected area and massage it gently into the skin. Leave it on overnight and rinse it off in the morning. Repeat this process daily until the infection clears up.
Aloe Vera:
Aloe vera has soothing and healing properties that can help relieve itching and inflammation associated with tinea barbae. Apply fresh aloe vera gel directly to the affected area and leave it on for 20-30 minutes before rinsing it off with water. Repeat this process several times a day until the symptoms improve.
Maintain Good Hygiene:
Maintaining good hygiene practices can also help prevent and treat tinea barbae. Keep the affected area clean and dry, avoid sharing personal items such as razors or towels, and wash your hands frequently to prevent the spread of infection.
While natural remedies can be effective for mild cases of tinea barbae, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional if you have severe symptoms or if the infection doesn’t improve with home treatment.
Good Hygiene Practices
Practicing good hygiene habits can help prevent the spread of Tinea Barbae and reduce the risk of recurrence. This includes regularly washing the face and neck with a gentle cleanser, avoiding sharing grooming tools, and keeping the beard area clean and dry.
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about tinea barbae
Tinea on the face, including tinea barbae, is primarily caused by dermatophyte fungi such as Trichophyton and Microsporum. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments and can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected individual or contaminated objects.
Tinea capitis affects the scalp and hair follicles, while tinea barbae specifically targets the bearded area of the face and neck. Both conditions are caused by dermatophyte fungi but differ in their location and presentation.
In some cases, mild cases of tinea may resolve on their own without treatment, especially if the immune system is able to effectively combat the fungal infection. However, seeking prompt treatment is recommended to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
While mild cases of tinea may spontaneously resolve, seeking treatment is advisable to expedite healing, alleviate symptoms, and prevent the spread of infection. Without treatment, tinea infections can persist and potentially worsen over time.
The strongest treatment for tinea depends on the severity and location of the infection. In many cases, topical antifungal medications such as clotrimazole, ketoconazole, or terbinafine are effective for mild to moderate infections. For more severe or resistant cases, oral antifungal medications such as griseofulvin or fluconazole may be necessary. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized treatment recommendations.
Conclusion
Tinea Barbae is a common fungal infection that affects the bearded area of the face and neck. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage and prevent this condition effectively.
