Phrynoderma also known as toad’s skin, because it like strawed like tode. Phrynoderma is a dermatological condition that often goes unnoticed but can have significant implications for those affected. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of Phrynoderma, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, preventive options, and prevention strategies.
What Causes Phrynoderma?
Nutritional Deficiencies and Their Impact
Phrynoderma is commonly associated with vitamin deficiencies, particularly vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, and vitamin B complex. This is seen in the extensor surface of the limbs and trunks, commonly in the former. These deficiencies can result from inadequate dietary intake, malabsorption issues, or certain medical conditions.
Other Contributing Factors
Apart from nutritional deficiencies, factors such as poor hygiene, excessive sweating, exposure to harsh environmental conditions, and genetic predisposition can also contribute to the development of Phrynoderma.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Skin Changes
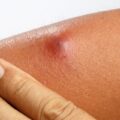
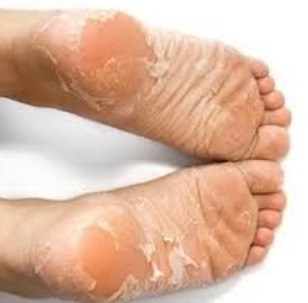
One of the hallmark signs of Phrynoderma is hyperkeratosisis also seen in myxoedema, which leads to thickened and rough skin, especially on areas prone to friction or pressure, such as the elbows, knees, and palms.
Additional Symptoms
Patients with Phrynoderma may also experience dryness, strawed, scaling, itching, and discoloration of the affected skin.
Many times this symptoms occurs in one knee, the other knee also occurs, and if it occurs in one elbow, it occurs in the other elbow.
Diagnosing Phrynoderma: What to Expect
Clinical Evaluation
Diagnosing Phrynoderma typically involves a clinical evaluation by a dermatologist. The doctor will examine the skin changes, inquire about the patient’s medical history, and may perform additional tests to rule out other possible conditions.
Differential Diagnosis
Phrynoderma must be differentiated from other dermatological conditions with similar symptoms, such as eczema, psoriasis, and keratosis pilaris.
Treatment Approaches: Targeting the Root Cause
Nutritional Supplements
Addressing underlying nutritional deficiencies is crucial in managing Phrynoderma. Patients may be prescribed vitamin supplements to replenish their nutrient levels.
Lifestyle Modifications
Encouraging good hygiene practices, maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding prolonged sun exposure, and wearing protective clothing can aid in preventing and managing Phrynoderma.
Prevention Strategies: A Holistic Approach
Balanced Diet
Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and leanproteins is essential for maintaining optimal nutritional status and preventing Phrynoderma.
Hydration
Staying hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water daily supports skin health and overall well-being.
Regular Skin Care
Adopting a regular skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and sun protection can help keep the skin healthy and resilient.
Here are the answers to your FAQs:
Phrynoderma can be associated with a deficiency in essential fatty acids, particularly linoleic acid.
Frog-like skin disease, also known as phrynoderma, is a dermatological condition characterized by thickened, rough skin resembling the texture of a frog’s skin.
No, phrynoderma is not contagious. It is a non-infectious skin condition primarily caused by nutritional deficiencies and other contributing factors.
The skin of a toad serves several functions, including protection against predators, regulation of water and electrolyte balance, respiration, and thermoregulation.
Yes, the skin of some toad species contains toxins that can be poisonous if ingested or if there is direct contact with mucous membranes or open wounds. However, not all toad species are equally toxic.
Toad skin is not typically dry but rather moist and glandular. The presence of glands secreting mucus helps to keep the skin moist, aiding in respiration and maintaining skin health.
Conclusion: Empowering Knowledge for Better Skin Health
Phrynoderma is a condition that warrants attention due to its potential impact on skin health and quality of life. By understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, prevention options, and prevention strategies, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining healthy skin and overall well-being.